FARMAKOEKONOMIKA. Modern Pharmacoeconomics and Pharmacoepidemiology
The journal is the first and most reputable in Russia and EurAsEC (Eurasian Economic Community) countries peer-reviewed periodical that publishes materials on new medical technologies, economic optimization of drug therapy, quality-of-life and healthcare problems.
The journal was founded in 2008.
The impact factor of this journal, as shown in the Russian Science Citation Index (RSCI) is the highest among the periodicals in the areas of pharmacoeconomics, health technology assessment, and epidemiology. According to RSCI, the biennial impact factor (without self-citations) was 0.325 in 2013, 0.411 in 2014, and 0.722 in 2015.
The journal publishes various materials on pharmacoeconomics and pharmaco-epidemiology including the methodology, data analysis and results of studies on public health, medical technologies and economic aspects of drug therapies. The original articles and literature reviews cover Cost-of-Illness Analysis, Cost-Minimization Analysis, Cost-Effectiveness Analysis (CEA), Cost-Utility Analysis (CUA), Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA), Quality of Life Assessment (QoL), Patients' Preferences & Patients’ Satisfaction indices and related topics.
Our aims and priorities focus on scientific and information support to the decision-makers and experts in public drug supply, health providers, research and education professionals, as well as pharmaceutic and insurance companies.
Languages: Russian, English
Periodicity: 4 issues per year (quarterly).
Copies of this journal are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License: full-text materials are freely available to the public in an open access repository.
Distribution of the printed version: Russia, the EurAsian Economic Community countries (Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Armenia, Moldova)
The editorial board of “FARMAKOEKONOMIKA. Modern Pharmacoeconomics and Pharmacoepidemiology” includes leading experts in pharmaco-economics, clinical pharmacology, medical technology assessment, epidemiology, and public health from Russia, USA and Spain.
The editorial board maintains the policy of full compliance with all principles of publishing ethics. Our ethical standards and codes conform to those of top international science publishers.
All submitted materials undergo a mandatory double-blind peer review.
Media Certificate of Registration: ПИ №ФС77-32713 of August 01, 2008.
ISSN 2070-4909 (Print)
ISSN 2070-4933 (Online)
By the decision of the Higher Attestation Commission (HAC) of Russia, “FARMAKOEKONOMIKA. Modern Pharmacoeconomics and Pharmacoepidemiology” is included in the "List of top peer-reviewed scientific journals and publications" where scientists seeking academic degrees are required to publish their results.
The journal appears in the Russian Universal Scientific Electronic Library (RUNEB) elibrary.ru and is also present in the database of the Russian Science Citation Index (RSCI). Concise versions of major articles from this journal are published by the All-Russian Institute for Scientific and Technical Information (VINITI). The journal is also indexed by "Ulrich's periodicals Directory" – a global information system of periodicals and continued publications.
Current issue
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
What is already known about thе subject?
► The number of registered biosimilars of original drugs based on monoclonal antibodies is increasing
► Pharmaceutical market shares are redistributing in favor of biosimilars of Russian companies
What are the new findings?
► Calculation of the difference in weighted average price between original drugs and their biosimilars, as well as of the reduction in expenses for drug procurement was performed
► The selection and prioritization of biosimilars procurement were justified as an effective tool for optimizing budget expenditures within public procurements of medicines
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The introduction of biosimilars will expand access to advanced treatment methods, providing more patients with the necessary therapy at equal budget costs
► Cost savings from the use of biosimilars will create opportunities for investment in new medical technologies and improve clinical infrastructure
Background. The increasing number of registered biosimilars of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) is altering the structure of the pharmaceutical market by amplifying the share of domestic manufacturers. Therefore, investigating their economic effect appears highly relevant.
Objective: To examine the impact of biosimilars on the market for public procurement of medicinal products based mAbs during the period 2022–2023.
Material and methods. A list of registered drugs based on mAbs was compiled from the State Register of Medicines and the Unified Information System for Procurement databases. The study involved statistical and marketing methods, including normalization of drug costs to weighted average prices (rub/mg), ABC analysis to identify key positions based on expenditure, and competitive analysis to categorize drugs as either original or biosimilars.
Results. The analysis of weighted average prices for original drugs and biosimilars, as well as their procurement volumes, demonstrated a significant economic effect on the health care system. The greatest savings were achieved through the procurement of bevacizumab and pembrolizumab biosimilars, resulting in savings of 15.1 and 3.8 billion rubles, respectively. In the group of rituximab drugs, procurement of biosimilars led to savings of approximately 2 billion rubles.
Conclusion. The introduction of biosimilars into the public procurement market has significantly optimized costs, thereby increasing patient access to life-saving medicines. The results emphasize the necessity for further development of biosimilars market to enhance the efficiency of public procurement and improve drug accessibility. However, a comprehensive understanding of their economic advantages require clinical studies that confirm the efficacy and safety of biosimilars in real-world clinical practice.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a serious medical and social problem worldwide. The average disability rate among DM patients reaches 39%
► DM is among the top 3 “expensive” nosologies; approximately 115 billion USD are spent on fighting it worldwide. In Russia, from 2023 to 2025, the costs of drug therapy for DM from the state budget amounted to 30 billion rubles
► Pharmacoepidemiological analysis of population consumption of drugs can be used to improve drug provision for patients
What are the new findings?
► The products assortment and sales volumes of drugs used to treat DM in pharmacies of all federal districts of the Russian Federation were analyzed for the period 2020–2023
► The features of population consumption of drugs used to treat DM were studied in the context of Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical classification subgroups, international nonproprietary names, and trade names
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The obtained data can be applied by health care managers to calculate the need for drugs prescribed for DM treatment
► The results of the study can be used in the development of federal and regional programs for preferential drug provision for DM patients
Objective: to study the characteristics of the population consumption of medicines for the treatment of diabetes mellitus (DM), sold in the retail sector of the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation (RF).
Material and methods. The study analyzed data on products assortment and sales volumes for drugs used to treat DM (according to Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATС) classification) through pharmacies in all federal districts of the RF for the period 2020–2023. In particular, the following ATС groups were studied: A10A, A10B, H04AA and A16AX (thioctic acid), as well as “sibutramine + metformin” combination prescribed to correct obesity in DM patients. The results were obtained on basis of comparative, retrospective, logical, and graphical methods as well as content analysis, data grouping in accordance with ATС groups, and descriptive statistics.
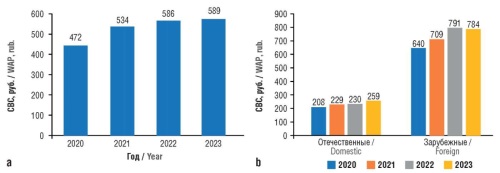
Results. In the retail sector of the pharmaceutical market of the RF, 54.9 million packages of antidiabetic drugs were sold for 32.4 billion rubles from 2020 to 2023. In the structure of sales in monetary terms, the share of Russian-manufactured drugs amounted to 16–17% approximately, and in physical terms, i.e. by the number of packages, it reached 37–39%. Throughout the analyzed period, the weighted average price (WAP) per 1 package of a drug for DM treatment increased from 472 to 589 rubles. Concurrently, as of year-end 2023, WAP per 1 package of an imported drug was 3 times higher than WAP of a domestic drug (784 and 259 rubles, respectively). In 2023, more than 45% of pharmacy sales in physical terms accrued to drugs of the ATC subgroup A10BA Biguanides (metformin), and about 25% to A10BB Sulfonylurea derivatives (glibenclamide, gliclazide, glimepiride, etc.). In 2023, the highest sales in monetary terms accrued to methsopamine, daphgylflozin, tytochotic acid, empagliflozin and gliclazide. In the structure of retail sales of drugs for DM treatment, fixed combinations accounted for about 15%. Despite an increase in the number of trade names of fixed combinations (from 24 in 2020 to 30 in 2023), their share in the product assortment structure remained insignificant, that did not comply with international recommendations for DM treatment.
Conclusion. Using pharmacoepidemiological monitoring tools, the features of the population consumption of drugs prescribed for DM treatment in the retail sector of the pharmaceutical market of the RF were studied in a retrospective aspect (for the period from 2020 to 2023). The contribution of ATC subgroups to the retail sales structure was established. It was revealed that the share of combined drugs was not more than 15% in the total retail sales structure that did not comply with international recommendations on DM treatment.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Somatostatin analogues have proven their сlinical efficacy in acromegaly treatment
► According to the Russian Registry of Hypothalamus and Рituitary Tumors, remission of acromegaly is achieved only in 24% of patients receiving prolonged-release octreotide and in 52% of patients receiving lanreotide
► Despite the higher cost of lanreotide compared to octreotide, lanreotide may have an advantage due to administration convenience and high efficacy
What are the new findings?
► A pharmacoeconomic comparative study was carried out to compare two modelled strategies of acromegaly treatment (using prolonged-release octreotide and lanreotide), taking the costs of treating disease relapses into account
► The analysis of direct medical costs required for a 2.5-year treatment course using the drugs under study in the context of the Russian healthcare system was conducted
► The results of the cost-effectiveness analysis for each of the two strategies were presented, taking into account the costs in the case of achieved remission
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The model constructed based on real clinical practice data demonstrates the advantage of lanreotide, thus being useful for clinicians when selecting a medication for acromegaly treatment
► The data on the economic feasibility of selecting lanreotide treatment in acromegaly patients can be used by healthcare managers and healthcare economists
► The study forms the basis for further pharmacoeconomic research of acromegaly treatment
Background. Pharmacoeconomic aspects of somatostatin analogues remain an important topic for discussion. Despite the higher cost of lanreotide compared to octreotide, the former may have an advantage in terms of administration convenience and high efficacy.
Objective: to carry out a cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) of the use of lanreotide and prolonged-release octreotide in adult patients with acromegaly.
Material and methods. A cost model for the treatment of acromegaly patients during the period of 2.5 years was developed, accounting for direct medical costs for drugs and surgical intervention. A pharmacoeconomic study by the CEA method and a sensitivity analysis of the model were performed.
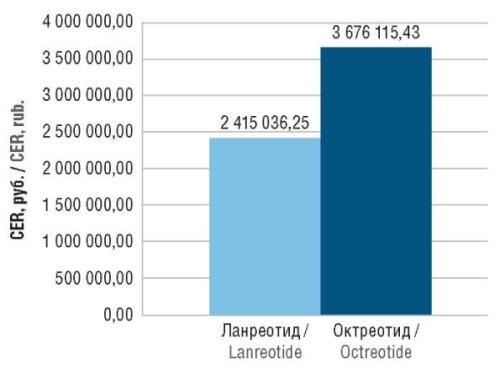
Results. In real clinical practice of acromegaly treatment, lanreotide enables a more effective remission compared to prolonged-release octreotide (51% vs 24%) under a comparable safety profile. The direct medical costs for a 2.5-year course of lanreotide amounted to 1,466,669.49 rubles per patient with acromegaly compared to 908,272.53 rubles for a course of prolonged-release octreotide. Considering the difference in the amount of 558,096.79 rubles, the course of lanreotide was found to be 25% more expensive. According to CEA results, the cost of achieving remission in 1 patient with acromegaly with lanreotide and prolonged-release octreotide was equal to 2,415,036.25 and 3,676,115.43 rubles, respectively. Therefore, over the period of 2.5 years, the cost saving amounted to 1,261,079.17 rubles (52%). The sensitivity analysis demonstrated the robustness of the initial model against an increase in the price of lanreotide up to 64%, an increase in the frequency of surgery in patients receiving lanreotide up to 302%, and a decrease in the frequency of remissions in patients receiving lanreotide up to 35%.
Conclusion. The use of lanreotide in adult patients with acromegaly is a clinically and cost-effective approach in the context of the Russian healthcare system.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Methotrexate (MTX) is a first-line treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) due to its high efficacy and favorable safety profile
► Pharmacoepidemiological studies demonstrate drug consumption trends and prescribing patterns among patients with rheumatological diseases
What are the new findings?
► Using ATC/DDD analysis a significant increase in MTX consumption for RA and PsA patients in the Kaliningrad Region of Russia between 2018 and 2023 was shown
► The main therapeutic combination in 55.8% of patients was “MTX +
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs”, which emphasize the need for a comprehensive approach to treatment
► A need to prescribe MTX in therapeutic doses reaching 25 mg/week for more effective disease control and minimizing additional risks associated with combination therapy was noted
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The results of the study may help in developing practical recommendations for more effective use of MTX in clinical practice
► Understanding prescribing patterns will help in optimizing pharmacotherapy with high levels of comorbidity
Background. Pharmacoepidemiological studies play a key role in optimizing pharmacotherapy for various diseases. In particular, significant progress in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) necessitates a detailed analysis of the consumption of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. The current therapeutic concept for these conditions focuses on achieving and maintaining longterm remission, which positions methotrexate (MTX) as a first-line agent characterized by high effectiveness, safety and advantageous pharmacoeconomic profiles.
Objective: To investigate the characteristics of MTX use in real clinical practice among patients with RA and PsA during outpatient medical care.
Material and methods. The study comprised two parts: a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of MTX consumption dynamics in 2018, 2020, and 2023 via ATC/DDD (Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical classification, ATC; defined daily dose, DDD) methodology, and a longitudinal, noninterventional, pharmacoepidemiological study conducted in 2023 using the medical information system “BARS. Healthcare”.
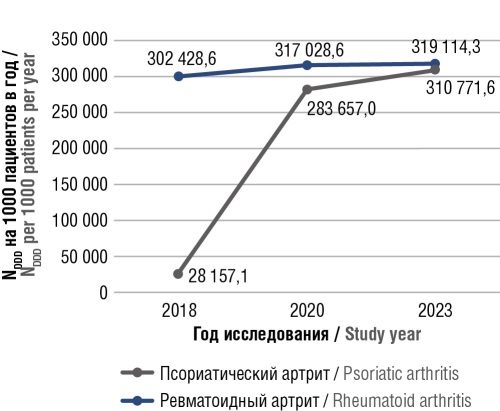
Results. The ATC/DDD analysis demonstrated a significant increase in MTX consumption among patients with RA and PsA: from 302,428.6 to 319,114.3 DDDs per 1,000 patients per year for RA, and from 28,157.1 to 310,771.6 DDDs per 1,000 patients per year for PsA in 2018 and 2023, respectively. The most frequently prescribed dose of MTX was 15 mg/week. The primary therapeutic combination for 55.8% of patients was “MTX + nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs”, with 32.7% of patients also receiving glucocorticoids (GCs) as part of this combination. The study identified a high frequency of prescriptions for proton pump inhibitors, GCs, and cholecalciferol, highlighting the activity of diseases under consideration, potential complications, and the necessity for the prevention of clinically significant drug interactions.
Conclusions. The conducted study confirmed that MTX remains the main drug for the treatment of RA and PsA. The ATC/DDD analysis demonstrated a significant increase in MTX consumption in recent years, correlating with its therapeutic effectiveness and accessibility. The high frequency of concomitant prescriptions underscores the complexity of treating RA and PsA and the need for an interdisciplinary approach to ensure safety and efficacy of the therapy.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Physiological functions of nitric oxide (NO) in endothelial support and prevention of endothelial dysfunction are very diverse
► The previously conducted systematic computer analysis allowed us to identify the most important areas of clinical research on the relationship between NO exchange and nutrients
► In addition to directly affecting NO biosynthesis, exogenous molecules can affect the endothelium indirectly, for example, through glycocalyx
What are the new findings?
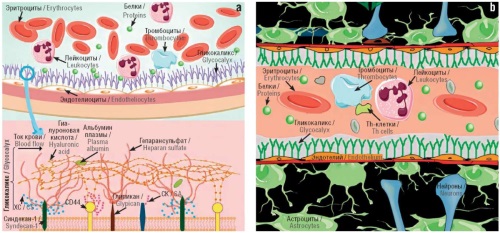
► The importance of glycocalyx as a regulator of endothelial function was demonstrated (especially considering its high representation in venous, arterial and capillary vessels)
► It was shown that glucosaminoglycan sulodexide is a promising agent for the treatment of endothelial dysfunction, promoting restoration of the structure and function of glycocalyx
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Dietary, pharmacological and nutraceutical approaches that normalize NO homeostasis show great promise for the treatment of endotheliopathy
► Sulodexide is the best molecule for affecting the endothelium, as well as the glycocalyx
Background. Nitric monooxide (NO) is a signaling molecule that plays an important role in many physiological processes, including the regulation of vascular tone, neurotransmission, immunity, mitochondrial respiration, and skeletal muscle contractility. Certain molecules, which are micronutrients or active ingredients of a number of drugs, improve NO biosynthesis and secretion.
Objective: systematization of information on the impact of various molecules on the modulation of NO levels in normal and pathological conditions.
Material and methods. An array of all currently available publications on fundamental and clinical studies of the effects of various molecules on NO levels was studied. By the query “nitric oxide” in the PubMed/MEDLINE database of biomedical publications 198,480 articles were detected, and by the query “nitric oxide AND endothelium” 27,869 articles were found (with a peak in 2005). After loading this sample, a systematic analysis of these 27,869 publications was performed using topological and metric approaches.
Results. As a result of systematic analysis at least 123 molecules were identified, that, in one way or another, modulate NO biosynthesis in the body. Molecules that improve NO metabolism can be conditionally divided into four groups: (1) macro- and micronutrients; (2) components of natural extracts; (3) medicines; (4) molecules that affect nitric oxide metabolism through the reparation of glycocalyx damage. Of the above variety of molecules that affect endothelium and NO biosynthesis, sulodexide stands out (by its effect on the endothelium and glycocalyx).
Conclusion. The use of sulodexide (a mixture of glycosaminoglycans with a high degree of pharmaceutical standardization) is one of the promising areas of therapy for endothelial dysfunction through the regeneration of glycocalyx, which is accompanied by the restoration of NO biosynthesis.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) is a chronic glomerular disease. It is one of the leading causes of terminal renal failure, which requires expensive renal replacement therapy
► IgAN research involves studying enterorenal etiopathogenesis, with a focus on the role of the intestinal MALT under the effect of food antigens (e.g., gluten)
► Patients with IgAN often exhibit isolated elevations in the serum levels of antigliadin antibodies
What are the new findings?
► The obtained results indicate the possibility of using IgA antibodies to deamidated peptides as a risk marker for IgAN progression
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Further studies into the effect of food antigens on the immune response in IgAN may help to develop additional personalized diagnostic and therapeutic approaches aimed at regulating the intestinal MALT and managing the highly active course of IgAN
Background. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) is a serious medical problem reported to be one of the most common causes of terminal renal failure. Current research increasingly focuses on the role of intestinal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) in IgAN pathogenesis, especially under the effect of food antigens, such as gluten. Patients with IgAN often have IgA antibodies to deamidated gliadin peptides (antiDGP IgA). Studying their isolated carriage can help in the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic methods aimed at regulating intestinal immune response and managing the highly active course and progression of IgAN.
Objective: To establish the clinical and diagnostic role of anti-DGP IgA in IgAN patients for the development of additional personalized clinical approaches and optimization of treatment strategies.
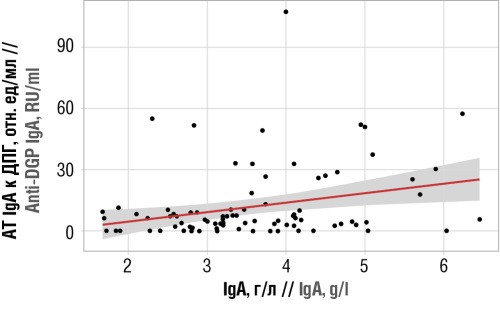
Material and methods. A total of 105 IgAN patients aged 18 to 64 years participated in the controlled, prospective, comparative, cohort study. Demographic, anamnestic, clinical, and treatment data were used. The blood of patients was tested for celiac-specific antibodies: anti-DGP IgA, IgA antibodies to tissue transglutaminase (anti-TTG IgA), IgA antibodies to endomysium. As a result, patients were divided into two groups depending on the presence of anti-DGP IgA: the main group (n=20) comprising IgAN patients with detected antibodies and the control group (n=85) consisting of patients seronegative for celiac antibodies. One patient was seropositive for both anti-DGP and anti-TTG IgA.
Results. As compared to the control group, the patients of the main group exhibited higher IgAN activity, which was assessed in terms of morning proteinuria (0.96 [0.70–1.60] g/l; p=0.005), daily proteinuria (1.50 [0.70–2.50] g/day; p=0.014), erythrocyturia (20.00 [15.00–25.00] per high power field; p=0.015), as well as levels of systolic (147.65±12.06 mm Hg; p=0.001) and diastolic (94.35±12.78 mm Hg; p=0.006) blood pressure. The detection of anti-DGP IgA was associated with a high concentration of serum IgA (4.35±1.06 g/l; p < 0.001). The direct correlation between anti-DPG IgA and IgA (ρ=0.247; p=0.020) can most likely be attributed to the hyperreactivity of IgA-producing B-lymphocytes of the intestinal mucosa in response to gluten. In the main group, the risk of a 50% decrease in the estimated glomerular filtration rate or progression to terminal renal failure within 5 years after the performed renal biopsy was statistically significantly higher than in the control group (15.05% [9.32–20.91] vs. 7.99% [4.97–11.73]; p=0.015).
Conclusion. The obtained results indicate the possibility of using anti-DGP IgA as a potential risk marker for IgAN progression. Further studies into the effect of food antigens on the immune response in IgAN opens up new prospects for the development of effective treatment methods.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Cancer patients show a high risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), during chemotherapy in particular, which requires reliable risk stratification for timely prevention of thrombotic complications
► VTE risk is assessed using various scores, such as Khorana, Vienna CATS, and TiC-Onco, however, their sensitivity and specificity are limited
► Although the Khorana score has been extensively used, a number of studies showed its limited performance in identifying patients at a high risk of thrombosis. This score overestimates the role of general clinical factors while neglecting individual biomarkers and characteristics of coagulation
What are the new findings?
► It was shown that a mismatch between von Willebrand factor (vWF) and ADAMTS13 ensyme activity should be considered as a pathogenetically significant mechanism of thrombosis formation in cancer patients
► The vWF/ADAMTS13 ratio largely reflects the degree of hemostasis regulation disorder and can serve as a marker of prethrombotic state during chemotherapy
► Inclusion of genetic and biochemical markers in the TiC-Onco score improves its sensitivity but reduces its specificity due to the detection of “silent” forms of thrombophilia
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Inclusion of the vWF/ADAMTS13 ratio in risk stratification algorithms support a more accurate identification of patients requiring thromboprophylaxis, thus avoiding unnecessary prescription of anticoagulants
► Modification of the existing risk scores with the inclusion of individual hemostatic parameters will improve the accuracy of risk assessment and provide a more personalized approach to VTE prevention
► Implementation of laboratory assessment of imbalance between vWF and ADAMTS13 may extend the standard list of examinations in the management of cancer patients with a high risk of thrombosis
Objective: To compare the diagnostic accuracy of the Khorana, Vienna CATS, and TiC-Onco scores in assessing the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with malignant neoplasms of the female reproductive system and mammary gland and to evaluate the prognostic role of the vWF/ADAMTS13 ratio in identifying groups with a high risk of thrombosis.
Material and methods. The study included 108 female patients with confirmed malignant neoplasms of the reproductive system and mammary gland (stages I–III), who were assessed for VTE risk using the Khorana, Vienna CATS, and TiC-Onco scores. In all the patients, the levels of von Willebrand factor (vWF) and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with a thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13 (ADAMTS13) were measured followed by calculation of their ratio. According to the final points obtained by each score, the patients were classified into the subgroups of a high, medium, and low risk of thrombosis. Concurrently, the presence of earlier thrombosis was analyzed. The sensitivity and specificity of the identified threshold values were assessed.
Results. According to the Khorana score, 33 patients scored ≥3 points, of which 24 had thrombotic complications. The Vienna CATS score, due to the inclusion of the D-dimer level, demonstrated a slightly higher detection rate of true thrombogenic cases (54.2% instead of 50%); however, the performance of this score in differentiation between false positive and false negative cases was not always high. The TiC-Onco risk score, which includes genetic markers of thrombophilia, increased the proportion of high-risk detection in VTE patients (up to 64.6%), although increasing the proportion of false positive cases, i.e. patients without thrombosis who formally got high scores. The vWF/ADAMTS13 threshold ≥1.6 showed the highest specificity (only 8.3% of false positive cases) and detected 70.8% of truly thrombogenic episodes, which indicates a high sensitivity of this marker.
Conclusion. The Khorana, Vienna CATS, and TiC-Onco scores demonstrate moderate accuracy in predicting thrombosis in cancer patients, partly due to their inability to consider the individual characteristics of endothelial dysfunction and/or overestimation of the impact of “silent” genetic mutations. Inclusion of the vWF/ADAMTS13 ratio in the observation algorithm, particularly at a threshold value of ≥1.6, provides for a clearer VTE risk stratification, thus showing promise as a priority criterion when deciding on antithrombotic therapy in patients with malignant neoplasms of the female reproductive system and mammary gland.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Spiramycin is a natural antibiotic from the macrolide group (with a 16-membered macrocyclic lactone ring). Macrolides have a very high level of safety and are generally well tolerated by patients of various ages
► Compared to other macrolides, spiramycin is characterized by less pronounced side effects, including not only negative impact on the gastrointestinal tract, but also allergic reactions and the consequences of negative effects on ion channels that support mineral metabolism and electrical potential of the cell
What are the new findings?
► Chemomicrobiomic and pharmacoinformatic profiling of spiramycin indicated significant differences between this molecule and the comparison molecules in terms of mechanisms of action, efficacy and safety
► Chemomicrobiomic analysis of the effects of the studied antibiotics on the average of the studied sample of strains of a number of pathogenic flora representatives showed that the antibacterial action of spiramycin is not inferior to the comparison antibiotics (and for some strains, it is superior)
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The significant difference in the chemogenomic, chemomicrobiomic and pharmacoinformatic profiles of spiramycin from other antibiotics (including other macrolides) suggests low resistance to spiramycin at the population level
Background. Antibiotics have different spectra of action on bacterial pathogens, including their antibiotic-resistant strains. Establishing the spectra of action of antibiotics and mechanisms of resistance to them is an important task for finding effective and safe antibiotic therapy.
Objective: a chemoinformatic study of the macrolide spiramycin in comparison with moxifloxacin, josamycin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin.
Material and methods. The analysis was carried out using modern data analysis methods (theories of labeled graph analysis, metric data analysis, combinatorial solvability theory, topological theory of ill-formalized problem analysis) developed within the algebraic approach to recognition.
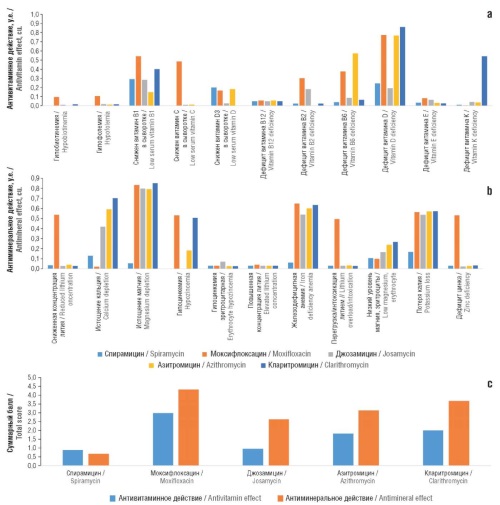
Results. Chemomicrobiomic and pharmacoinformatic profiling of spiramycin indicated significant differences between the spiramycin molecule and the comparison molecules in terms of efficacy, safety and mechanisms of action. Characteristic features of spiramycin action were inhibition of protein synthesis by influencing the ribosome, with possible inhibition of bacterial topoisomerase, DNA synthesis and with anti-membrane activity, including through ionophore mechanisms. Analysis of correlations between chemogenomic profiles of molecules indicated a pronounced similarity of the effects of three of the five studied molecules (josamycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin) with a significant difference in the effects of spiramycin from the effects of other studied macrolides. Mechanisms of resistance to spiramycin potentially include genes from the functional groups “assembly of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria”, “sorbitol transport”, “transmembrane transporter of L-leucine”, etc. Spiramycin was characterized by the best safety profile in terms of antimicronutrient effects (increase in the risk of excretion of a particular micronutrient by only 7%).
Conclusion. The significant difference between the chemogenomic, chemomicrobiomic and pharmacoinformatic profiles of spiramycin and other antibiotics (including other macrolides) suggests low resistance to spiramycin at the population level.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Terpenes and phytosterols exhibit anti-hyperlipidemic effects by reducing cholesterol absorption, improving lipid metabolism, and adjusting lipoprotein levels
► Clinical studies showed that phytosterols are capable of reducing low-density lipoprotein levels by 5–15%, with a higher intake resulting in a larger decrease. They may lead to a slightly decrease in triglyceride levels, particularly in hypertriglyceridemia
What are the new findings?
► The anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-hyperlipidemic properties of terpenes and phytosterols extracted from Iraqi chickpeas were evaluated in animal experiments, revealing their potential as bioactive substances
► Histopathological examination showed significant improvement in the state of hepatocytes and cardio-myocytes in the mice groups receiving terpenes and phytosterols in comparison with the non-treated mice group
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The use of terpenes and phytosterols from Iraqi chickpeas could significantly impact therapeutic practice, potentially leading to new treatment approaches for hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular conditions, and metabolic illnesses
► Terpenes and phytosterols contained in Iraqi chickpea could be introduced in functional meals or supplements to treat hyperlipidemia and associated disorders; to that end, further clinical trials involving humans are required
Objective: To compare the amelioration effects of terpenes and phytosterols extracted from Iraqi chickpea on histopathological damage in mice fed on high-fat diet (HFD).
Material and methods. Whole chickpea plants of the Fabaceae family were collected during the flowering period in the northern area of Erbil. The collected plants were cleaned, dried in a shaded area at room temperature, pulverized with mechanical mills, and weighed. Experiments were conducted from October 2021 to April 2022. The research involved 32 healthy albino male mice 2–3 months of age, weighing about 20–30 g. The animals were provided by the Higher Institute for Diagnosis of Infertility and Assisted Reproduction Techniques. One week prior to the onset of the experiment, the animals were acclimatized to standard environmental conditions; food and water were provided ad libitum. HFD (2% cholesterol and 1% peanut butter) was added to the standard diet for 28 days to induce hyperlipidemia. In all experimental groups, the body weight was measured weekly. The terpenes and phytosterol fraction extracted from Iraqi chickpea was administered for 28 days via an intragastric tube. Mice were kept fasting for 24 hours and blood samples were extracted via heart puncture. Standard diagnostic kits and an automated analyzer were used for estimation of serum total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoproteins (LDL), very lowdensity lipoproteins (VLDL), high-density lipoprotein, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and total serum bilirubin (TSB) levels. The animals were sacrificed, then their liver and heart organs were removed for assay.
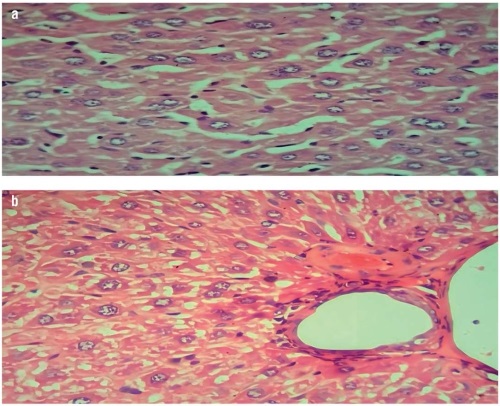
Results. Histopathological examination of the hyperlipidemic mice group showed a marked and diffused cytoplasmic fatty infiltration of hepatic and cardiac cells. These effects were successfully ameliorated by administration of terpenes and phytosterols, although treatment with terpenes seemed to be more effective than that with phytosterols. In comparison with phytosterol treatment, terpene treatment in HFDinduced hyperlipidemic mice led to an improvement in lipid profiles, manifested in a highly significant decrease (p≤0.05) in the serum levels of TC (142.40±14.43 mg/dl), TG (98.89±8.71 mg/dl), LDL (79.43±15.14 mg/dl), and VLDL (19.78±1.74 mg/dl); with a highly significant (p≤0.05) decrease in the liver enzymatic activities of (ALT (19.19±1.36 U/l), AST (15.98±1.3 U/l), and ALP (20.99±4.43 U/l)) and TSB levels (1.60±0.12 mg/dl) (highly significantly differences with p≤0.05). Terpenes also led to a statistically significant improvement in the level of tissue malondialdehyde and glutathione in hyperlipidemic mice (p≤0.05).
Conclusion. In comparison with phytosterols, terpenes exhibit a highly significant ameliorating effect in HFD-induced hyperlipidemia, improving the state of liver and heart tissue, lipid profile, liver function enzymes, and oxidative stress parameters. Further research should assess the efficacy of terpenes and phytosterols and to elucidate the mechanism of their anti-hyperlipidemic action.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about thе subject?
► Introduction of new technologies for data transmission and processing, as well as the creation of new approaches to the treatment of diseases determine changing in the conduction of clinical trials (CTs)
► Trends in conducting CTs are related to their decentralization and the complication of protocols, as well as other opportunities provided by modern technologies
► The emergence of hybridoma technologies and gene correction technologies serves as a vector for the development of treatment and diagnostic methods, which have now reached clinical stages. An increasing number of CTs are being launched in this direction
What are the new findings?
► Based on the results of the review of materials, two large groups of CT tendencies were identified for the first time: one is related to the organization and conduction of CTs and the other is associated with development of innovative drugs
► In the group of tendencies related to CT organization and conduction, 18 directions and subgroups were identified
► In the group of tendencies related to the development of innovative drugs, two large-scale trends were identified
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The identified trends allow us to make long-term prognoses in planning various areas of medical activity, as well as to expect the emergence of methods for treating diseases that until recently were considered incurable
► Trends in CT organization indicate the possibility of accelerated introduction of new drugs to the market with higher reliability of data on efficacy and safety
Background. The clinical trial (CT) industry is subject to changes, some of which are rapidly developing and their directions can be predicted, while others develop gradually, forming stable tendencies, which requires analysis to confirm and predict them. According to the generally accepted time gradation, there are an operational (up to 1 month), short-term (up to 1 year), medium-term (up to 5 years), long-term (up to 20 years), and long-term (over 20 years) prognoses. A short-term forecast is common in CT industry.
Objective: to identify trends in the development of CT industry until the end of 2024.
Material and methods. We searched publications in Russian and English segments of the Internet in open access sources in ClinicalTrials.gov, PubMed/MEDLINE, Google Scholar, Academia, ResearchGate, CyberLeninka, eLibrary databases by key query “trends in clinical trials” for the period from January to March 2023. The query “history of clinical trials” was also used in Russian part of the Internet through Google search. The analysis included publications on the history of CT development over 1936–2023. The total number of sources analyzed was 59 (9 Russian and 50 English).
Results. The tendencies in CT development can be divided into two groups. The first one is related to CT organization and conducting, while another is associated with development of innovative drugs. In the first group, the trends have persisted since 2022 and are expressed in the ongoing digitalization of operational activities, a shift from centralized research to decentralization, while the protocol design has changed towards patient-centricity. In the second group, the number of expected drugs has decreased and a shift towards biological drugs, gene and cell therapy has become more pronounced.
Conclusion. Trends in CI are characterized by a number of innovations, primarily related to digitalization, the development of telemedicine technologies, mathematical modeling, artificial intelligence, virtual CI, decentralization and patient-centricity.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Artificial intelligence (AI) is actively implemented in medicine, which provides more accurate diagnostics and effective treatment of various diseases
► Machine learning and deep learning are used to analyze clinical data, predict the development of diseases and their complications, and develop telemedicine technologies
► The effectiveness of AI in medicine is assessed in terms of the error matrix, weighted errors, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, area under curve, and the Youden index
What are the new findings?
► The potential of AI was analyzed, and examples of its successful application in some areas of medicine were given (e.g. cardiology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, dermatovenereology, neurology, hematology, nephrology, oncology and orthopedics, rheumatology)
► The study results were presented, which indicate the high effectiveness of AI as compared to conventional diagnostic methods
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The use of AI in medicine can increase the diagnosis accuracy and treatment efficacy, which will improve the quality of medical care and reduce its costs
► Choosing the right approach to AI training in medicine can improve the diagnostic and treatment outcomes of various diseases
► The results of applied research show that AI can be used in the form of computer programs and smartphone applications as well as in telemedicine services as part of the clinical decision support system
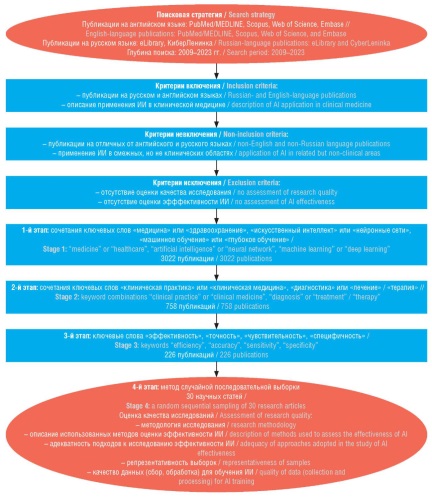
Objective: To examine the effectiveness of using artificial intelligence (AI) in clinical medicine (in terms of accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity).
Material and methods. The study involved a search and analysis of scientific publications examining various types of AI training and training approaches, as well as areas of AI application in clinical practice, which were submitted to PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, eLibrary, and CyberLeninka databases in 2009–2023. A sequential analysis of randomly sampled articles yielded 30 publications on the use of AI in endocrinology (4 articles), dermatovenerology (3), cardiology (1), radiology (1), gastroenterology (1), neurology (5), hematology (5), nephrology (4), orthopedics and rheumatology (4), oncology (2).
Results. AI demonstrated sufficient effectiveness: accuracy ranged from 49% to 99%, sensitivity from 42% to 100%, and specificity from 48% to 100% in such areas as cardiology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, dermatovenereology, and radiology. In some cases, AI was more effective than clinical diagnostics by medical specialists, e.g. in detecting melanoma and diagnosing atrial fibrillation.
Conclusion. AI shows high diagnostic efficiency, increases accuracy and speeds up diagnostic search, which makes it promising to expand the use of AI in clinical medicine.
What is already known about the subject?
► Phenol and parabens exhibit bactericidal properties and are used as stabilizers/preservatives
► When analyzing drugs, it is necessary to pay close attention not only to the active substance, but also to the choice of preservatives used in injection forms
► The long-term effects of phenols/parabens as preservatives have not been studied
What are the new findings?
► Systematization of studies indicated a complex estrogen-like and antiandrogenic effect of phenol derivatives (including parabens), stimulation of oncogenesis pathophysiology by phenol/parabens
► Basic and clinical studies demonstrated teratogenic and other toxic effects on the embryo and negative effects of phenol/parabens on the health of pregnant women
► Long-term negative effects of phenol/paraben exposure on children were shown
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Large-scale clinical studies of longitudinal and cross-sectional design are needed to assess the long-term toxic effects of phenol and parabens
► Stabilization of medicines with phenol or parabens is an outdated pharmaceutical technology, which is important to consider when doctors analyze the drug composition
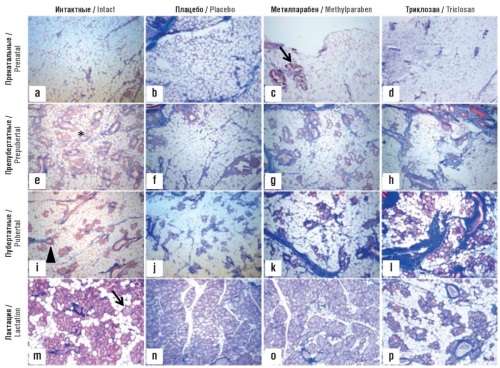
Background. Phenol and parabens exert bactericidal properties, are relatively low-toxic (in acute toxicity tests) and are used in pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries as stabilizers/preservatives for the final product. Despite their widespread use, the long-term toxicological effects of phenol and parabens remain largely unexplored.
Objective: To conduct an analysis of the results of basic and clinical studies on chronic toxicity of phenol and parabens.
Material and methods. The study included 544 articles found using the query “Preservatives, Pharmaceutical [MeSH Terms] AND Phenol [MeSH Terms]” in the PubMed/MEDLINE biomedical publications database. Methods of topological and metric analysis of big data were applied, developed in the scientific school of Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences Yu.I. Zhuravlev. Keywords were sorted by empirical Rudakov–Torshin informativeness functionals in the context of combinatorial theory of solvability, followed by combinatorial testing of solvability to find terms with the greatest informativeness.
Results. Despite the existence of individual studies on the acute toxicity of phenol and its derivatives (including parabens), the chronic toxicity of phenol and parabens remains poorly understood. This fact is indicated not only by a lack of carefully performed research, but also by the information in safety data sheets supplied by manufacturers of the relevant substances. The associations of phenol and paraben blood levels with certain chronic pathologies in humans have been insufficiently studied. At the same time, the authors of fundamental research, if not “sound the alarm,” then strongly underline the need to conduct large-scale clinical trials on the long-term toxic effects of phenol and parabens. Firstly, this is due to complex estrogen-like effect of phenol and parabens, including (1) effects on estrogen sulfotransferases, (2) direct interactions with estrogen receptors, (3) influence on the expression of steroid receptor genes. Secondly, the available data from fundamental research indicate that phenol/parabens obviously stimulate the the molecular mechanisms of oncogenesis pathophysiology (systematic disturbances in gene expression and corresponding changes in the structure of organ tissues). Thirdly, teratogenic and other toxic effects on the embryo and pregnancy were demonstrated not only in experimental studies (neurotoxicity and teratogenesis in animal models), but also in clinical observations (metabolic disorders in a pregnant woman, including the metabolism of purines and fatty acids beta-oxidation, hyperactivity and/or excess body weight in children, asthma, thyroid dysfunction, etc.).
Conclusion. Findings from basic research and selected clinical studies dictate an urgent need to examine the association of phenol/paraben blood levels with chronic pathologies in large-scale clinical trials with cross-sectional and longitudinal design. The lack of indication on toxic effects of parabens and phenols in certain clinical studies may just be an artifact of incorrect data analysis.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2070-4933 (Online)