ORIGINAL ARTICLES
What is already known about thе subject?
► During implementing High-Cost Nosology (HCN) Program difficulties regularly arise upon the distribution of limited financial resources for satisfying the requirements of all patients
► Many researchers have repeatedly considered options for solving this problem and assessed the activity within the HCN Program as a whole
What are the new findings?
► The changes were shown in weighted average price per 1 unit of measurement on drugs included in HCN Program due to centralization of procurements, starting from 2019
► The changes have been demonstrated in procurement structure within HCN Program over 2019–2022, particularly due to centralization of procurements for new drugs and nosologies
► The ratio of the procurement volume between nosologies has been traced in each year under considered period (from 2019 to 2023), and the annual additional growth in each nosology has been determined
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The data obtained can be used to solve the difficulties associated with the financial restrictions of HCN Program by assessing the real effect of drug procurement centralization and proper distribution of financing between drugs within the individual nosology
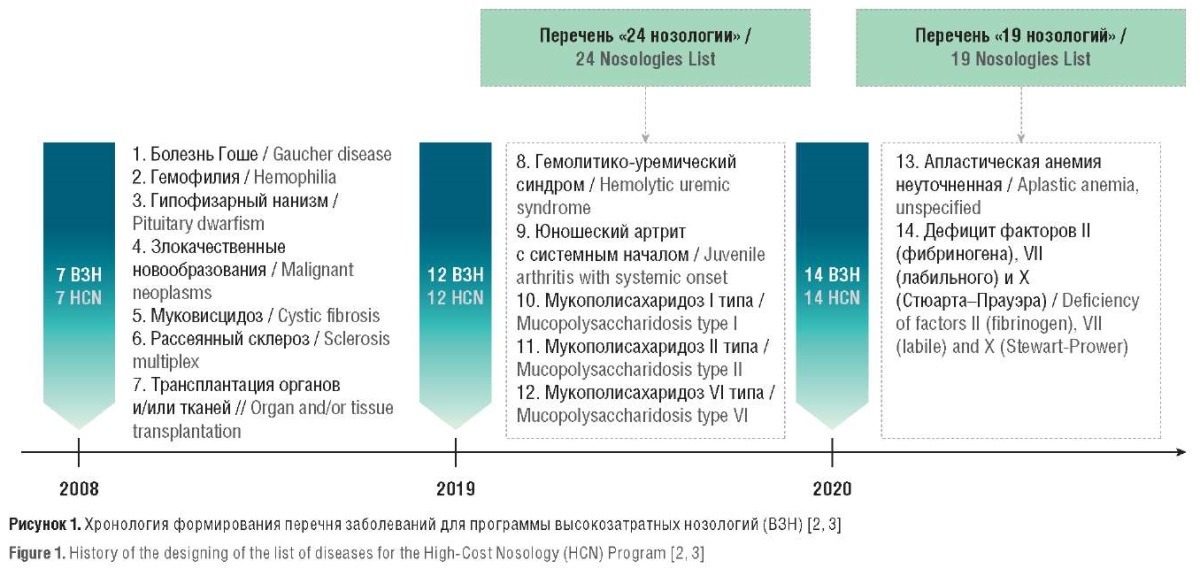
Background. In the Russian Federation, patients receive expensive drugs from the federal budget funds within High-Cost Nosology (HCN) Program.
Objective: to assess the impact of drug procurement centralization on the weighted average price (WAP) per 1 unit of measurement (UM) of a drug, the procurement structure within HCN Program over 5 years (2019–2023), as well as the annual volume of procurements for each nosology and the additional annual growth compared to the previous year.
Material and methods. The data on public procurement within HCN Program, regional and federal drug provision programs over the specified time period have been analyzed. During the analysis of individual nosologies, 22 drugs for the treatment of 12 HCN have been considered.
Results. The median value of the change of WAP per 1 UM for all drugs within HCN Program was 6.01%. Aplastic anemia was characterized by the lowest volume of procurements over 5 years, while for malignant neoplasms was the largest. The growth in procurements from year to year within nosologies varied from +1% to +661%, while a decrease was from –97% to –1%.
Conclusion. The results can be used as a basis for further research related to the process of implementation of preferential drug provision, and to development of additional tools to improve the efficacy of pharmacotherapy choice for included drugs and management decisions regarding the further expansion of HCN Program.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Dyslipidemia holds a special place among the risk factors for atherosclerosis. This collective term reflects the excessive load of the body with atherogenic lipoproteins, which transforms into a systemic atherosclerotic process over time
► 2023 national guidelines and the opinion of leading Russian experts on the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of lipid metabolism disorders, which are typical for considerable proportion of Russian population, are aimed to reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular (CV) diseases and prolong human life
► In 2023, the SCORE2 scale was introduced in the clinical guidelines “Lipid metabolism disorders” (ID752) approved by the Scientific and Practical Council of the Ministry of Health of Russia but the required laboratory tests were not included in the system of prophylactic medical examination of the adult population
What are the new findings?
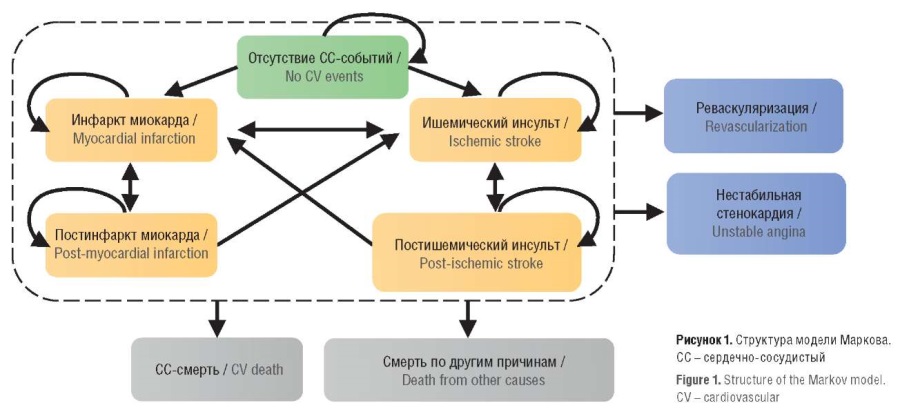
► Markov model was developed to analyze the economic consequences of including diagnostic tests (by SCORE and SCORE2 scales) in existing prophylactic medical examination programs, and to assess the costs and outcomes associated with pharmacotherapy in patients with different risk levels. The model describes the course of lipid metabolism disorders in adult patients aged 40–69 with high and very high risk of CV events according to the SCORE and SCORE2 scales without concomitant diseases identified during medical examination
► It was shown that using the SCORE2 scale instead of SCORE could lead to the reclassification of most patients with low and moderate risk of CV complications to high and very high risk groups. This will entail additional costs for laboratory tests within prophylactic medical exmination and for pharmacotherapy in cases of revealing lipid metabolism disorders
► The costs for lipid-lowering therapy were analyzed and presented in two scenarios which consider different sources of funding
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The implementation of the new SCORE2 scale may change the practice of prescribing lipid-lowering therapy, and dramatically increase the number of patients who will require earlier initiation of pharmacotherapy to prevent CV events
► Corrections in federal benefit drug provision programs for the primary prevention of CV events could be done based on the results of the presented analysis
Objective: to assess the demand for pharmacotherapy in risk groups on adverse cardiovascular (CV) events identified during prophylactic medical examination of the adult population according to the SCORE2 (Systemic Coronary Risk Estimation) scale, which is being introduced into clinical practice.
Material and methods. To analyze the economic consequences of including diagnostic examinations to assess the risk by SCORE and SCORE2 scales, a Markov model was developed, which described the course of lipid metabolism disorders in adult patients aged 40 to 69 years without concomitant diseases identified during prophylactic medical examination. The model cycle was 2 months (the average waiting time for response to therapy); the modeling horizon was 3 years; the calculated values were estimated for the period 2024–2026. The economic analysis of long-term consequences involved calculating the cost of pharmacotherapy and the costs associated with CV events at outpatient and inpatient stages of medical care. The costs of drug therapy were determined based on dosage regimens presented in instructions for medical use in Russia, and clinical guidelines.
Results. According to the modeling results, in the period 2024–2026, the administration of pharmacotherapy to reduce the risks of CV events will enable to achieve 23,224 potentially saved lives through exclusively government funding or 23,605 through mixed sources of funding (government and citizens’ own funds). The cost of the analyzed pharmacotherapy upon the introduction of the SCORE2 scale will be from 50.18 billion rubles (with government funding) to 318.14 billion rubles. Concurrently, pharmacocorrection will provide a reduction in the costs of inpatient treatment and outpatient medical services to 4.1 billion rubles due to the achieving of intended low-density lipoprotein level, and 1.6 billion rubles due to the achieving of intended triglyceride levels.
Conclusion. Using new SCORE2 scale may lead to changes in the practice of prescribing lipid-lowering prophylaxis of CV diseases, as well as to a sharp increase in the number of patients who may require earlier prescription of pharmacotherapy to prevent CV events.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Certain medical interventions require the expenditure of significant resources of the healthcare system, primarily expensive medical products and qualified personnel that can often be a limitation in providing such care to patients living in certain regions of the Russian Federation (RF)
► The existing regulatory framework for the healthcare system in the RF enables the centralization of medical care at the interregional level but the practice of such associations is small and limited to several regions
What are the new findings?
► The criteria were presented for selecting medical interventions that could be centralized based on individual interregional medical organizations (costs, complexity, and rarity)
► A methodology was proposed for identifying “centralization points” based on statistical analysis of hospitalizations
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The described approaches may influence the practice of organizing specialized medical care on certain areas in the territorial subjects of the RF towards centralizing rare high-tech care in certain medical organizations
Background. As new high-tech methods of treatment and diagnostics are introduced into the basic compulsory health insurance program, the focus on creating separate regional healthcare systems is becoming less effective. The creation of the necessary infrastructure requires disproportionately large investments, while the needs of the population in most regions do not provide adequate loading of newly created facilities. A promising solution to these problems is the centralization of delivering certain types of medical care (MC) on the basis of interregional medical centers.
Objective: development of approaches to identifying medical interventions that are appropriate to provide in specialized interregional centers.
Material and methods. The criteria for selection of medical interventions including MC profiles and diagnosis-related groups (DRGs) of diseases, which potentially require centralization were developed. On the basis of statistical analysis, data on specialized MC provided in inpatient settings by “Pediatric surgery” and “Traumatology and orthopedics” profiles were analyzed to identify regions with low and high levels of hospitalizations in order to determine the need for centralization or the creation of interregional centers.
Results. The analysis enabled to identify the territorial subjects of the Russian Federation (RF) where the issue of MC centralization would be relevant to increase its availability to the insured population in the territory of certain subject. Besides, the study identified regions, in which the number of hospitalizations significantly exceeded the average indicators in the RF. It is advisable to create interregional MC centers on the basis of such subjects.
Conclusion. The presented analysis of individual profiles and DRGs across the territorial subjects of the RF showed the objective differences in the extent of provided MC. The proposed methodology for determining DRGs and identifying subjects of the RF that have a surplus or deficit in the provision of MC can form the basis for approaches to identifying “MC centralization points”.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used for effective pharmacotherapy of inflammation and pain
► Long-term therapy and/or inappropriate using NSAIDs can lead to damage to the gastrointestinal tract
► New NSAIDs with distinctive profiles of their interaction with proteome proteins are being sought with regard to enhanced safety
What are the new findings?
► Using a conglomerate of methods for chemoinformatic analysis of molecules, assessments of the pharmacological effects of a perspective NSAID RRS-1 were modeled
► It was shown that RRS-1 could activate adenosine and dopamine receptors, cannabinoid receptor 2 and GABAA receptor to a greater extent than other molecules that corresponded to anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive and neuroprotective effects
► The RRS-1 substance had a moderate profile of antivitamin and antimineral actions attesting a moderate risk of side effects due to iatrogenic micronutrient imbalances
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Supplementing RRS-1 with a number of micronutrients at physiological doses will reduce the risk of loss of these micronutrients to zero
► Chemoproteomic profiling of the candidate molecule RRS-1 revealed a constellation of potential pharmacological properties that may enhance the analgesic effects of the compound in certain patient populations
Background. To plan effective and safe pharmacotherapy for inflammation and pain, it is important to evaluate the mechanisms and spectrum of action of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including their effects on human proteome.
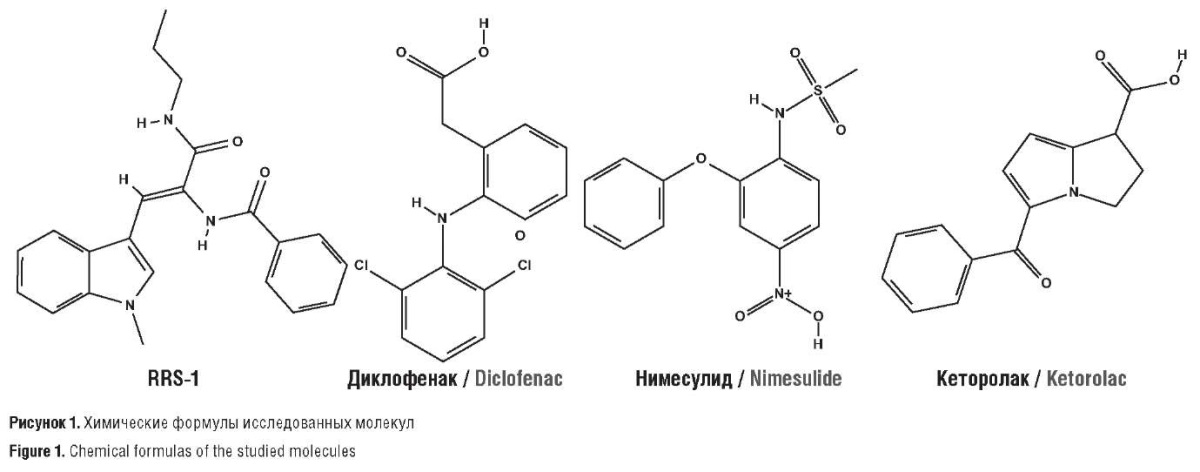
Objective: to identify and evaluate the most significant specific differences of candidate molecule RRS-1 (N-{(Z)-2-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)1-[(propylamino)carbonyl]vinyl}benzamide) from other NSAIDs through differential chemoreactome analysis.
Material and methods. Chemoproteomic modeling of pharmacological effects of RRS-1 molecule and a number of well-known NSAIDs (diclofenac, nimesulide, ketorolac) on human proteome was carried out on the basis of numerical prediction algorithms over the space of heterogeneous feature descriptions, developed in the topological approach to recognition by Yu.I. Zhuravlev and K.V. Rudakov scientific school.
Results. Significant differences in the effects of the studied molecules were found for 1232 proteins of human proteome. The features of assessing interactions of the studied molecules with 47 target proteins, which most distinguished the effects of RRS-1 molecule from all others were identified. RRS-1 could activate adenosine and dopamine receptors, cannabinoid receptor 2 and GABAA receptor to a greater extent than other molecules. Activation of these receptors corresponded to anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive and neuroprotective effects. RRS-1 could preferably inhibit a number of pro-inflammatory proteins, receptor bradykinin 1, metabotropic glutamate receptor 5, matrix metalloproteinases 8, 9, 12, and blood coagulation factor X. Additionally, RRS-1 molecule showed preferable inhibition of a number of kinases targeted in antitumor and anti-inflammatory therapy. RRS-1, less than other studied molecules, interacted with the receptors of vitamin D3, thyroid hormone, acetylcholine, cannabinoids and opioids, orexin, and various metabolic enzymes, which is important in assessment of the safety of using drugs based on this molecule. RRS-1 characteristically exhibited a moderate profile of antivitamin action: the total score of vitamin and mineral loss (7.4±3.7) was significantly less in comparison to diclofenac (11.7±4.5) and was actually on the same level as nimesulide (6.9±3.7) and ketorolac (6.7±3.6).
Conclusion. Chemoreactomic and chemoproteomic profiling of RRS-1 candidate molecule provided pre-experimental assessments of its efficacy and safety through modeling interactions with the human proteome.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Mango mistletoe (Dendrophthoe pentandra) is one of the semi-parasitic plants used in traditional therapy because of its great efficacy
► Tea mistletoe (Scurrula atropurpurea (Blume)) and Dendrophthoe pentandra combination have been known as a potential medicine for several diseases
What are the new findings?
► The administration of a combination of mistletoe extract with doses of 250, 500, and 1,000 mg/kg of body weight in rats did not show differences in total bilirubin, glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, glutamic pyruvic transaminase, albumin, cholesterol, and triglycerides serum levels, while serum levels of globulins, total protein, high-and low-density lipoproteins showed significant differences (p<0.05)
► It was shown that an increase in the dose of the mistletoe combination leads to the increase in number of pycnotic, karyorectic and karyolytic cells in the histopathological structure of rat liver
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► This study results might help to develop the optimal combination of methanolic extract Scurrula atropurpurea (Blume) and Dendrophthoe pentandra to maintain liver health
Background. Tea mistletoe (Scurrula atropurpurea (Blume)) and mango mistletoe (Dendrophthoe pentandra) have been known as a potential medicine for several diseases.
Objective: to investigate the effect of the combination of methanolic extract Scurrula atropurpurea (Blume) and Dendrophthoe pentandra (MESA-DP) on rat liver function and structure using serological and histopathological analysis.
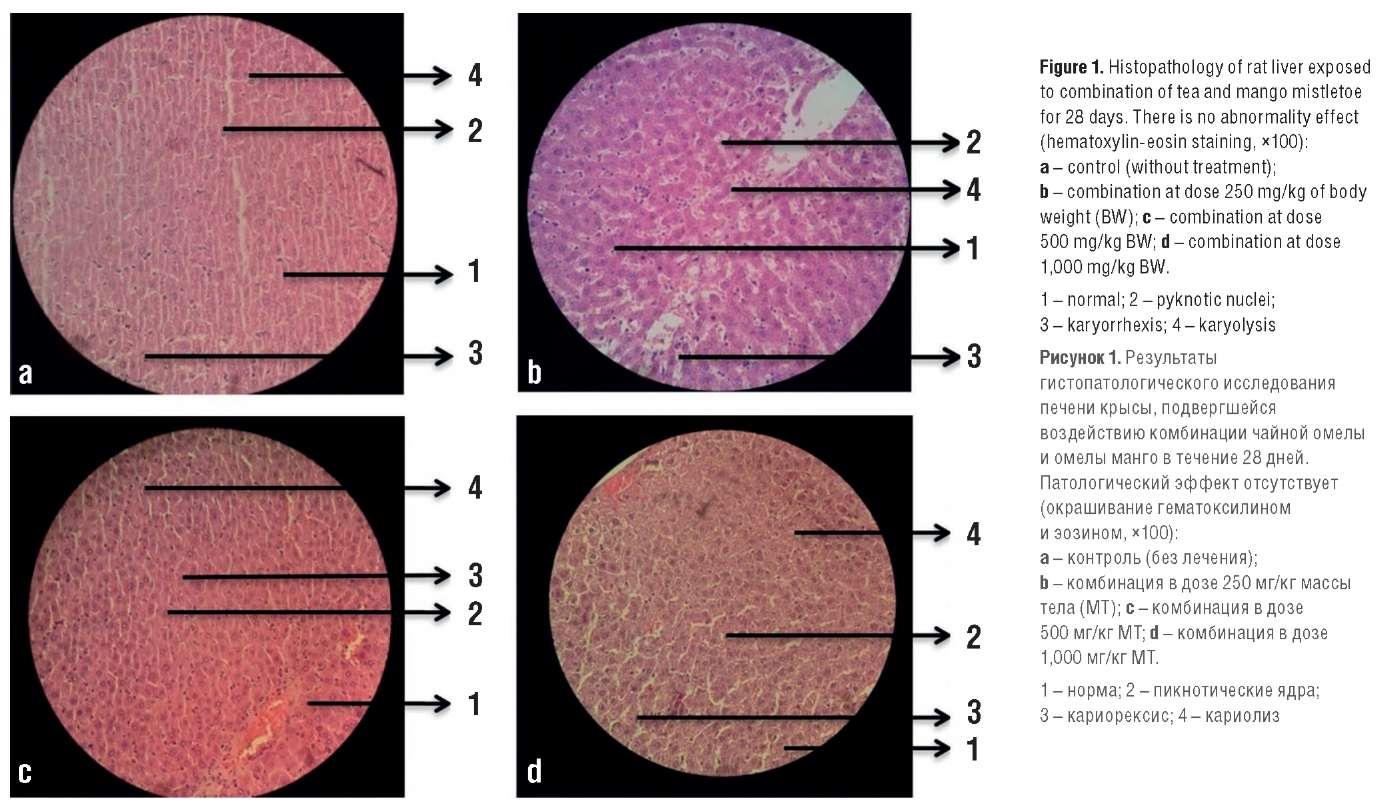
Material and methods. This study was experimental during 28 days using 20 rats divided into four groups (Group 1 as a control, while Groups 2, 3, and 4 were given MESA-DP at doses 250, 500, and 1,000 mg/kg of body weight, respectively). The liver histopathological structure was observed using hematoxylin-eosin staining. The liver function assessment included total bilirubin, serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), total protein, albumin, globulin, cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels. Data were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA analysis (ANalysis Of VAriance) and performed via SPSS Statistics 17.0 (IBM, USA).
Results. The administration of MESA-DP did not show significant differences at all doses for the liver rat function in total bilirubin, SGOT, SGPT, albumin, cholesterol and triglycerides (p>0.05), while globulin, total protein, HDL and LDL showed significant results (p<0.05). The liver histopathological structure showed the number of pyknotic, karyorrhectic and karyolytic cells in rats after MESA-DP administration compared to controls, which grew with increasing dose.
Conclusion. The liver function in rats after being exposed to MESA-DP was not affected in terms of total bilirubin, SGOT, SGPT, albumin, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. However, using MESA-DP increased the necrotic liver cells. It may be beneficial for the liver health of experimental animals taking into account the correct dosage.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Vitamin B12 is important for the maintenance of many processes (folate, homocysteine metabolism, DNA methylation)
► Targeted modulation of vitamin B12 derivatives through specific modifications of the corrin core makes it possible to obtain compounds with different pharmacological properties
► To adequately plan further experimental studies (in vitro, in vivo), it is first necessary to simulate the pharmacological properties of selected molecules in silico
What are the new findings?
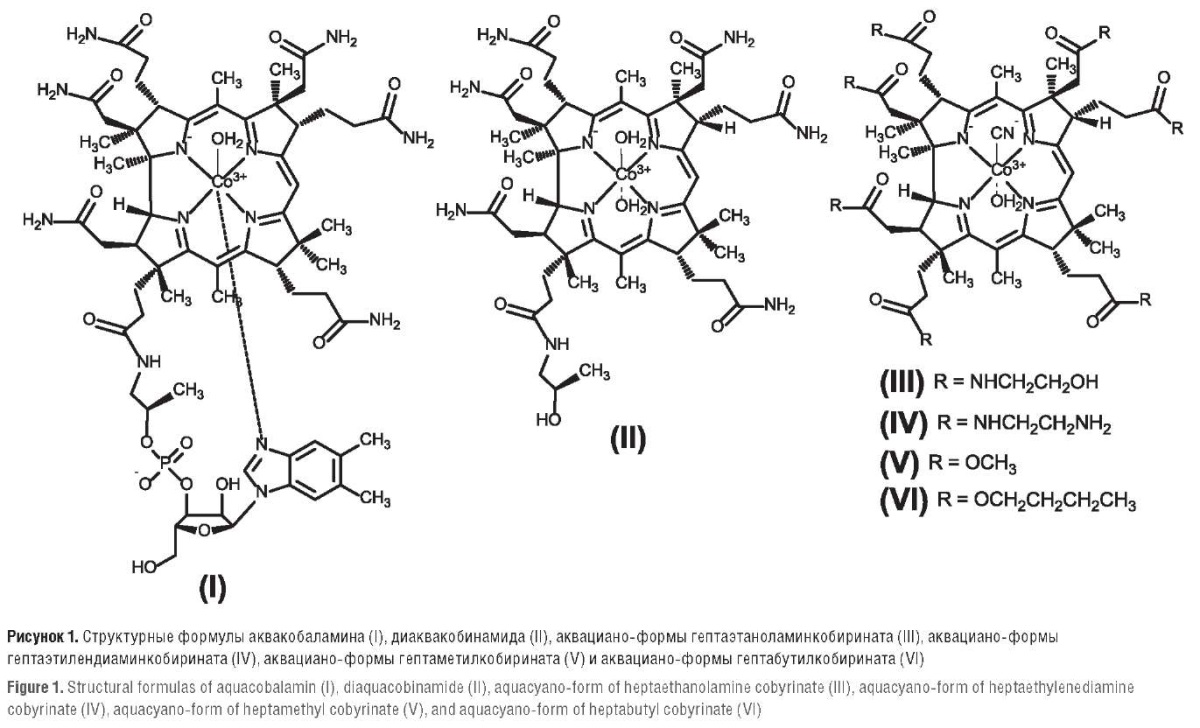
► Using chemoproteomic analysis, we obtained estimates of the interaction of six vitamin B12 derivatives (aquacobalamin, diaquacobinamide, cobyric amino alcohol, cobyric diamine, heptamethylcyanaquacobyric acid, heptabutylcyanaquacobyric acid), which were significantly different for 1,200 human proteome proteins
► Chemoproteomic profiles of each compound were grouped into three clusters of substances with similar properties (aquacobalamin, diaquacobinamide – cobyric amino alcohol – cobyric diamine, heptamethylcyanaquacobyric acid – heptabutylcyanaquacobyric acid)
► The established differences in the biological effects of the studied compounds relate to neuroprotective, neurotrophic, antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities. The mechanisms for realizing these pharmacological effects were described
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Interactions with specific human proteome proteins are important for modulating proteome activity and for targeted drug delivery
► Differences in neuroprotective, neurotrophic, antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities of the studied derivatives make it possible to plan experimental and clinical studies of these compounds more effectively
Background. Chemical derivatives of vitamin B12 are characterized by a wide range of pharmacological effects. It is important to learn how to establish relationships between changes of the corrin ring structure in vitamin B12 derivatives and changes in pharmacological properties.
Objective: to evaluate the interaction of six vitamin B12 derivatives (aquacobalamin, diaquacobinamide, aquacyano-forms of heptaethanolamine, heptaethylenediamine, heptamethyl and heptabutyl cobyrinates) with human proteome proteins.
Material and methods. Using the method of chemoinformational (chemoproteomic) analysis, implemented within the framework of algebraic recognition theory and topological data analysis, the constants of half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) and half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) of human proteome proteins were assessed.
Results. Significant differences were found in the interactions of the studied molecules with 1200 proteins. It was shown that the chemoproteomic profiles of each of the compounds form three groups of molecules with similar proteomic properties: (1) aquacobalamin, (2) diaquacobinamide, aquacyano-forms of heptaethanolamine and heptaethylenediamine cobyrinates, (3) aquacyano-forms of heptamethyl and heptabutyl cobyrinates. A more detailed analysis of the chemoproteomic profiles of the studied compounds using the GO (Gene Ontology) nomenclature of biological functions of proteins made it possible to identify functional GO categories indicating differences in the biological effects of the studied compounds: neuroprotective regulation of neurotransmitter activity (serotonin receptor activity, cholinergic synapses, regulation of dopamine secretion, receptor thyroid hormones), reduction of inflammation (inhibition of cytokine biosynthesis, including tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 beta, I-kappa-B kinases / nuclear factor kappa В, leukocyte migration), etc.
Conclusion. The profiles of differences in the pharmacological properties of the studied compounds with respect to their effects on neuroprotection, neurotransmitter metabolism, and inflammation were identified and described.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Vitamin B12 is important for folate metabolism, homocysteine, DNA methylation, inflammation reduction, antitumor protection by modulating the activity of proteome proteins
► Targeted modulation of the properties of vitamin B12 derivatives through specific modifications of the corrin core makes it possible to obtain compounds with different pharmacological properties
► To assess drug safety, it is important to simulate in silico pharmacologically promising candidate molecules, including evaluation of antioxidant properties and effects on micronutrient metabolism
What are the new findings?
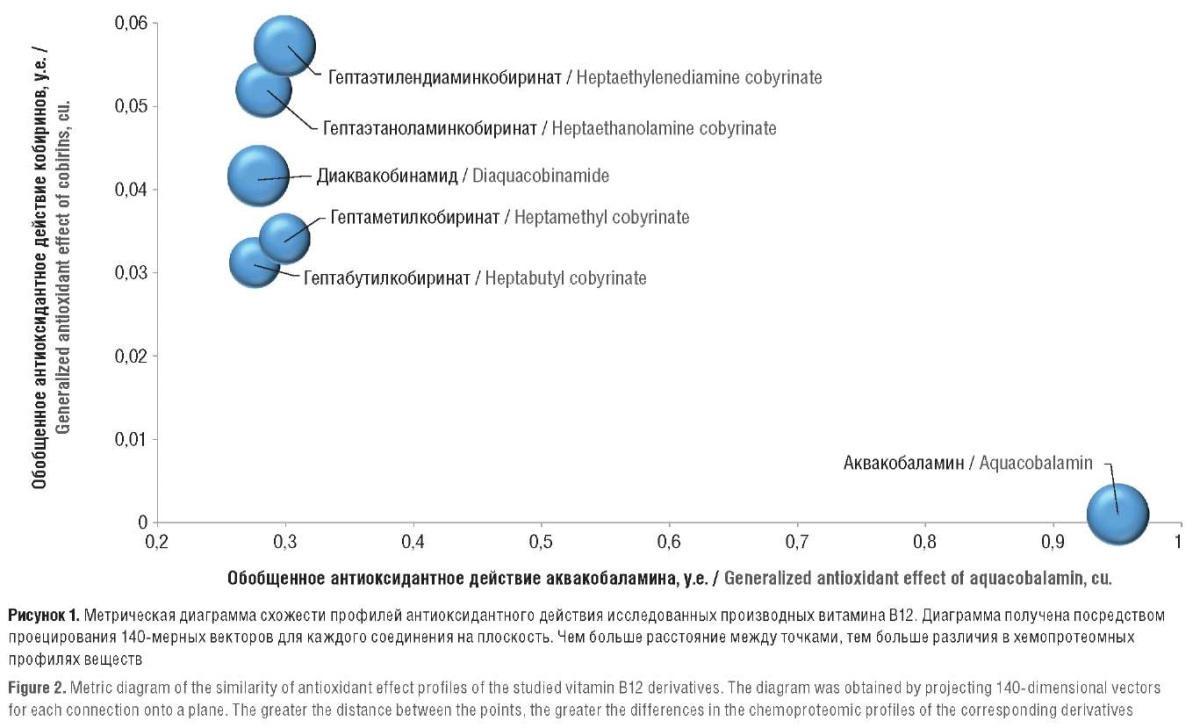
► Using the method of chemoproteomic analysis, estimates of 140 antioxidant properties of aquacobalamin, diaquacobinamide, aquacyanо-forms of heptaethanolamine, heptaethylenediamine, heptamethyl and heptabutyl cobyrinates were obtained
► All six chemical derivatives of vitamin B12 exert antioxidant properties, assessed by modeling various test systems (to the greatest extent, aquacobalamin)
► Aquacobalamin practically did not stimulate the loss of other micronutrients; the remaining molecules moderately affect the micronutrient balance (removal of magnesium, calcium, vitamins B1 and D3)
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Antioxidant properties of chemically modified forms of vitamin B12 may help reduce excess inflammation
► The antioxidant effects of vitamin B12 derivatives and their moderate effect on micronutrient metabolism may enhance their antitumor effect
Background. Synthetic derivatives of vitamin B12 exhibit various physical, chemical and pharmacological properties. The development of methods for predicting the properties of these molecules based on their chemical structure is important for the targeted organic synthesis of corrins with the desired properties and range of applications in pharmacology.
Objective: chemoreactomic assessment of the antioxidant effects of vitamin B12 and its derivatives: aquacobalamin, diaquacobinamide, aquacyano-forms of heptaethanolamine-, heptaethylenediamine-, heptamethyl- and heptabutylcobyrinates.
Material and methods. The study was conducted using the method of chemoreactomic analysis, implemented within the framework of the algebraic theory of recognition and topological data analysis and based on the theory of isomorphism of labeled graphs and modern methods for predicting numerical target variables. To carry out chemoinformatic chemoreactome analysis, a special problem-oriented theory was developed within the boundaries of the combinatorial theory of solvability and the antioxidant properties of vitamin B12 derivatives were assessed (140 activities in total).
Results. Significant differences were found in the properties of the studied substances in relation to oxidative stress. In test systems based on the oxidant 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl, at different exposure times to molecules (15–60 min) in different concentrations (10–125 μM, 50–3000 μg/ml), aquacobalamin exhibited the most pronounced antioxidant properties at lower concentrations (up to 100 µM). At higher concentrations of substances (125 μM), the antioxidant activity of other vitamin B12 derivatives was higher. All studied molecules had a moderate antimicronutrient effect (total score of about 3.0; for most synthetic drugs, this score is higher than 3.6). Aquacobalamin was characterized by the least pronounced antimicronutrient effect (total score less than 0.8), which indicates an almost complete absence of antivitamin and antimineral action, corresponding to an average increase in the risk of a particular micronutrient excretion by no more than 5%.
Conclusion. All the studied compounds exert antioxidant properties to one degree or another. Regardless of the choice of simulated test systems for assessing oxidative stress, aquacobalamin demonstrated antioxidant effects to the greatest extent and practically did not stimulate the loss of other micronutrients.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about thе subject?
► The development of pharmaeconomic analysis is moving towards the complication of the applied mathematical methods and software tools
► Among software tools in pharmacoeconomic analysis, fewer studies are based solely on calculations in Excel, and R scripting language with open source libraries is increasingly mentioned
► The flexibility of tools in R environment allows for pharmacoeconomic analysis of virtually any complexity
What are the new findings?
► A comparative analysis of 10 R software libraries for pharmacoeconomic analysis was conducted, including for assessing the quality of life based on standardized questionnaires, calculating indicators of economic effectiveness of medical interventions, conducting a sensitivity analysis of the effect of medical interventions based on decision tree algorithms and Markov models
► Based on the results of analysis of the possibilities for constructing pharmacoeconomic models of various types, it was shown which package commands should be used to generate primary data
► It was indicated which additional libraries need to be installed to visualize the results of pharmacoeconomic calculations and identify predictors of a patient's transition from one health state to another
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► A critical review of tools available in R environment will allow a more effective approach to the selection of methods of pharmacoeconomic analysis and libraries that most fully meet the needs of research and visualization of calculation results
Background. To reveal the full complexity of the relationship between medical intervention and disease outcome, new methods of analysis and modeling are actively being developed, and tools are becoming more complex, for the use of which it is important to understand their limitations and advantages.
Objective: conducting a critical review of the main open-source packages in R environment for conducting pharmacoeconomic analysis.
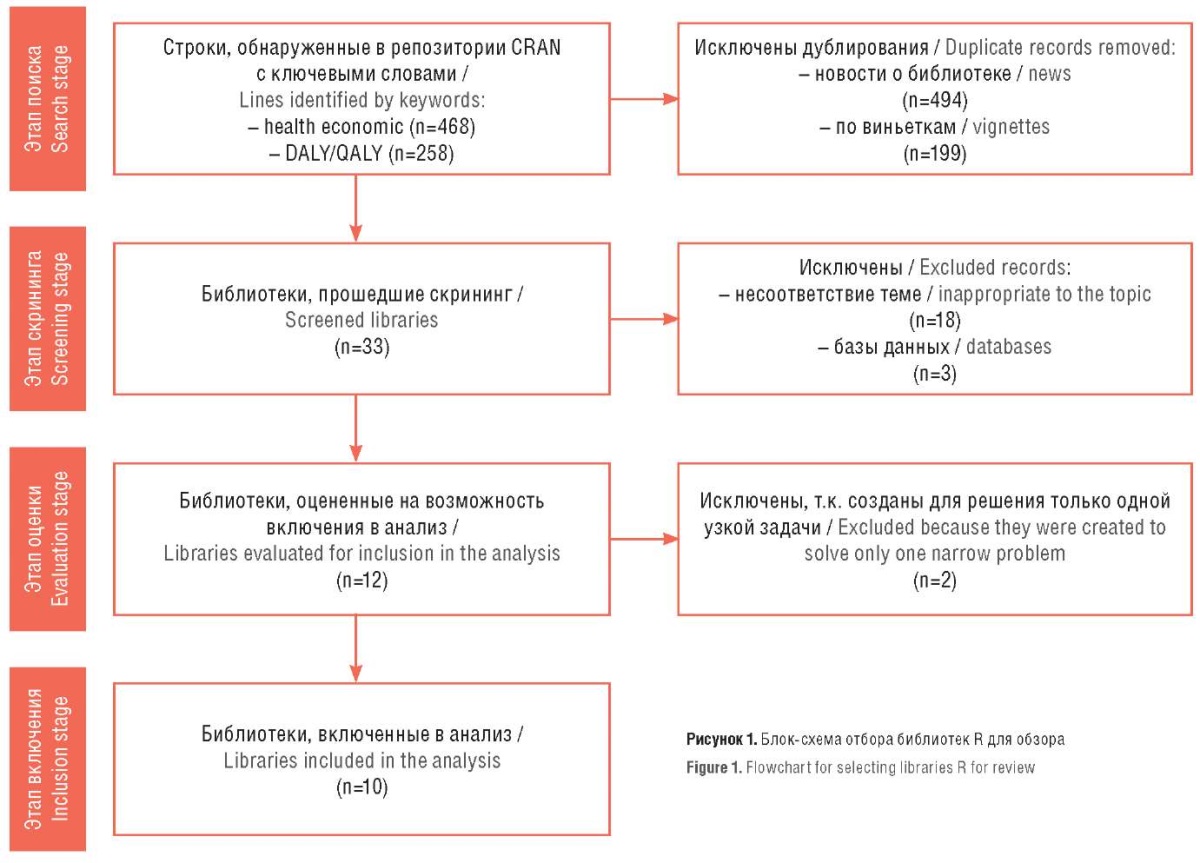
Material and methods. The selection of libraries used for pharmacoeconomic analysis in the R environment was carried out based on the keywords “health economic”, “DALY”, “QALY” in the CRAN repository. Only libraries that were valid on the date of the review were included in the study. The selected 10 R software libraries for pharmacoeconomic analysis were reviewed from the standpoint of the number of tools they support, the format of the data used, the possibilities of visualizing results and generating reports, the presence of vignettes and the possibilities of parallelizing calculations.
Results. The selected libraries can be divided into three classes: packages for calculating various quality of life indices, libraries for calculating indicators and indices of economic effectiveness of medical interventions (DALY, QALY, ICER), libraries for performing sensitivity analysis of the effect of medical interventions based on decision tree algorithms and Markov models. The libraries “heemod”, “hesim”, “rdesign” allow building simple Markov and semi-Markov models, but preference should be given to “heemod” due to the presence of vignettes. To conduct an analysis using cohort Markov models, partitioned survival models, it is recommended to use the “hesim” library, if there are gaps in the results, it is recommended to use “missingHE”. The “rdesigin” library allows building decision trees indicating the risk of developing certain conditions and the cost of therapy. The “survHE” library for survival analysis, used specifically in health economics, allows you to carry out probabilistic sensitivity analysis based on survival models. To calculate the survival models themselves to identify predictors of a patient's transition from one health state to another, you will need to additionally install the “flexsurv” library. To visualize the results of pharmacoeconomic modeling, you should additionally install the “diagram” and “ggplot2” libraries.
Conclusion. The conducted critical review of open source libraries in R environment can serve as a navigator for choosing a tool for performing pharmacoeconomic analysis.
What is already known about thе subject?
► The levels of a new biomarker сystatin C in blood serum (sCysC) and urine (uCysC) are affected by a number of physiological conditions and non-renal events
► sCysC level enables prediction of adverse outcomes, such as in-hospital and out-hospital mortality, chronicity of renal dysfunction, the demand and duration of renal replacement therapy
What are the new findings?
► Some non-specific factors, diseases and medications affect the sCysC level, but do not affect its prognostic and diagnostic value in acute kidney injury (AKI)
► High levels of sCysC and uCysC in patients with pneumonia associated with severe and extremely severe COVID-19 are statistically significant predictors of lethal outcome
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Despite the reactive changes of CysC levels in some diseases and conditions, it has proven itself as a reliable diagnostic and prognostic marker of AKI with high sensitivity and specificity
► uCysC is highly informative, and sCysC is informative predictor of mortality in pneumonia associated with severe and extremely severe COVID-19
The level of serum and urinary cystatin C (CysC) can be modulated by some factors (weight, gender, age, ethnicity, smoking), diseases (sepsis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, obesity, hypo- and hyperthyroidism) as well as administration of glucocorticosteroids, but all of them do not affect its prognostic and diagnostic value in acute kidney injury (AKI). The CysC concentration can predict adverse outcomes, such as in-hospital and out-hospital mortality, chronicity of renal dysfunction, the demand and duration of renal replacement therapy (RRT). The sCysC is an independent predictor of RRT completion in critically ill AKI patients.
What is already known about thе subject?
► The Beers criteria (BC) are the first expert consensus on the use of potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) for people over 65 years of age, the involvement of which in clinical practice enables optimization of drug therapy and leads to decreased incidence of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and improved health outcomes in the elderly population
► Since the ВС initiation in 1991 they have been updated seven times (the latest update was in 2023)
► ВС are actively used in practical healthcare in the USA, Australia, Canada, European countries, and Japan. A considerable number of domestic publications on the assessment of pharmacotherapy in elderly patients using BC only appeared after the update in 2015
What are the new findings?
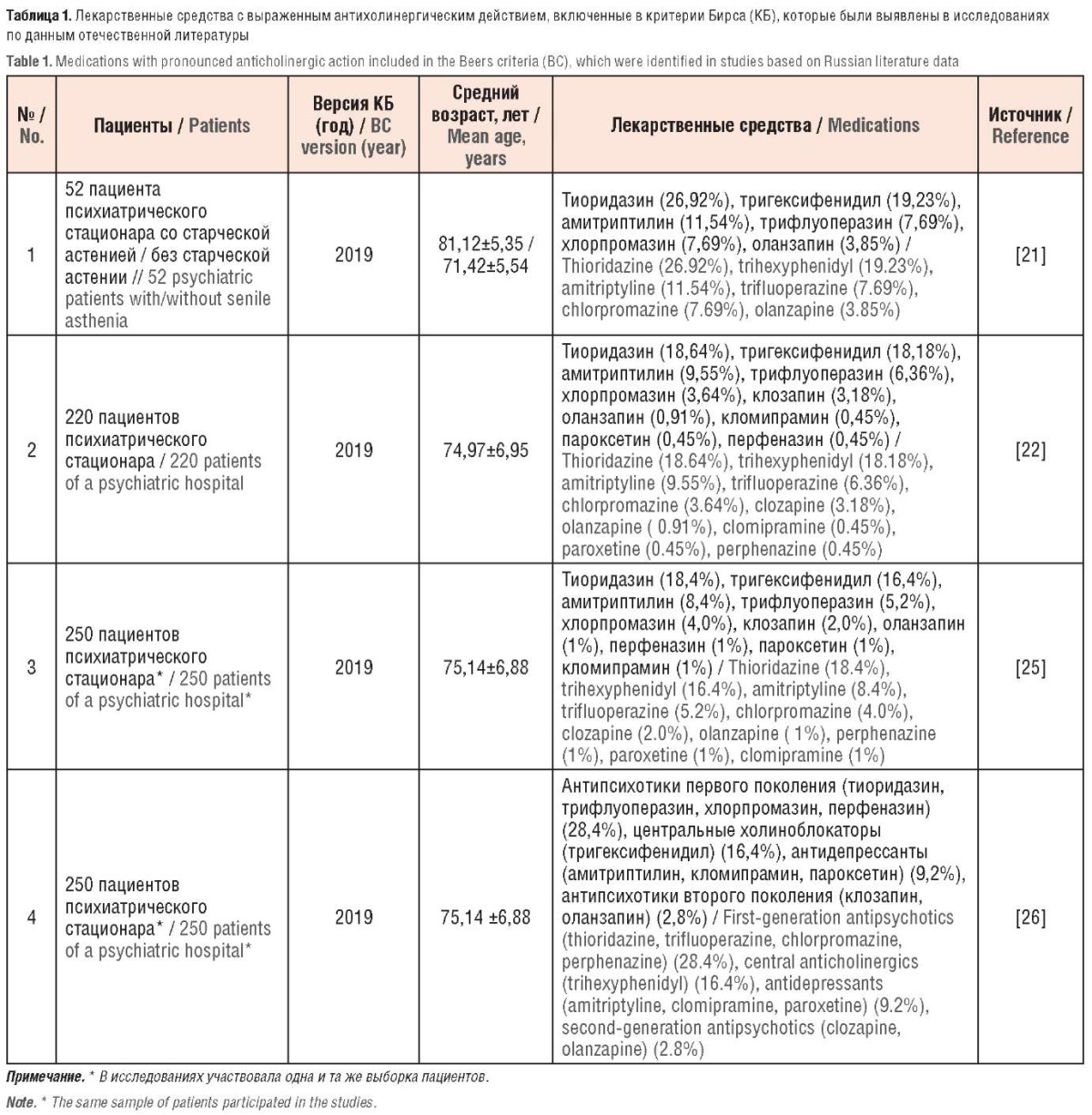
► It was shown that according to the BC in Russia, PIMs were most often prescribed in inpatient healthcare
► The experience of using BC in Russia as a tool for analyzing individual clinical cases of ADRs occurrence was reviewed. Two episodes of falls in elderly patients were detected, where a connection was found between developed ADRs and the prescription of PIMs (midazolam, spironolactone) from the BC list
► A study was presented, which revealed that antihistamine drug therapy, which did not contain PIMs according to the BC was economically accessible for elderly patients
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► This information will help medical professionals to be more alert to the most common PIMs in Russia, that may further prevent or reduce the number of ADRs and drug-induced conditions in elderly patients
► Drawing attention to the problem of high frequency of using PIMs may become an impetus for the introduction of “restrictive” lists, such as BC, into the work of doctors when prescribing and analyzing drug therapy for people aged over 65 years
► A promising direction in clinical practice would be the design of an electronic medical decision support system with integrated BC adapted for Russian conditions
Objective: analysis of domestic scientific literature to identify ways of applying the Beers criteria, frequency of prescriptions and the structure of potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) in elderly patients.
Material and methods. The search for publications was carried out in Google Scholar abstract database, as wel as in eLibrary and CyberLeninka information-bearing networks for the period from 2013 to 2023. In total, 34 articles were found, among which 18 sources used Beers criteria as a tool for identifying PIMs.
Results. In inpatient therapeutic departments, the maximum frequency of PIMs prescriptions according to the Beers criteria was 66.6% of cases, in surgical departments – 70%, in psychiatric departments – 90.4%, and in outpatient treatment settings – 28%. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs at different diseases were the most prescribed group of PIMs in both inpatients and outpatients. Surgical hospitals took the leading position in prescribing these drugs; specifically, more than 2/3 of elderly patients (75%) received them. According to two studies describing clinical cases of drug-induced falls in patients, the Beers criteria were effective in identifying drugs that can provoke this condition. One of papers presented application of Beers criteria to assess the economic affordability of replacing PIMs with safer new generation drugs.
Conclusion. An analysis of domestic literature data has shown various ways of applying the Beers criteria, the frequency of prescriptions, and the most common PIMs. This information will help healthcare workers to be more wary of such drugs and think over applying the Beers criteria in routine practice of geriatric patients, which will further prevent or reduce the number of adverse drug reactions.
What is already known about thе subject?
► In many regions of the world, there has been increased interest in using biologically active supplements (BAS) as alternative means of preventing and treating various diseases, as well as strengthening the immune system and minimizing the risk of possible complications of pharmacotherapy
► There is a need to develop global quality standards and address regulatory issues related to BAS production, since counterfeit or mislabeled products may circumvent current regulations, leading to increased negative consequences
► There is no international consensus on BAS, that may be due to differences in regulatory definitions and classifications
What are the new findings?
► The available foreign data on the regulation of BAS were analyzed, including a comprehensive review of legislative and regulatory issues in the USA, China, and the European Union. The structure and volume of the BAS market in countries, which mainly produce and import them as well as the profile of BAS users were assessed
► It was shown that to determine the reliability of biological effects as well as to assess the degree of BAS efficacy and safety the large-scale multicenter controlled comparative studies are necessary on different patient categories in addition to fundamental research aimed at identifying the mechanisms of BAS therapeutic action
► The need to create a unified BAS database and standardize approaches to conducting scientific research devoted to BAS biological effects was highlighted
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The development of evidence base on therapeutic and preventive effects of BAS will open the prospect of their introduction into new areas of medicine and health programs
The use of biologically active supplements (BAS) has gradually expanded over the past 20 years. The public health crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic as well as concerns about vaccines in many parts of the world have led to a particularly increased interest in using BAS as an alternative for protection and treatment of this new disease to strengthen the immune system and minimize the risk of possible complications. Abroad, as well as in the Russian Federation, there is a sharp increase in BAS sales. In this regard, questions arise about their impact on human health in general. Numerous scientific studies have demonstrated both the beneficial properties of BAS and their negative and even toxic effects. Besides, considering the global interest in this problem, there is a need to clarify the legal status of BAS. The object of this review was to summarize the available foreign data on the regulation of using BAS and the corresponding market trends, including a comprehensive analysis of the legislative and regulatory aspects of BAS in the United States, China, and the European Union. The structure and volume of the BAS market were assessed in countries, which primarily produce and import them, and the user profile was analyzed additionally.
What is already known about thе subject?
► The application of аrtificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare is already proving its efficacy in reducing errors and improving diagnostic accuracy
► AI is widely used to diagnose and predict diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular pathologies
► Various approaches to AI learning, including machine learning and deep learning, are applied for subsequent medical data analyzis
What are the new findings?
► The current achievements of AI in improving the quality of diagnosis and treatment of various diseases were presented
► The issues of data availability, bias and model interpretability which affect the AI efficacy were discussed
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The implementation of AI can significantly improve the diagnostic accuracy and reduce the time for processing medical data
► Automating routine tasks will allow physicians to focus on more complex and critical aspects of treatment
► AI can help in developing personalized therapy plans based on the results of patient examination that will improve treatment outcomes
Objective: to explore the potential and challenges of artificial intelligence (AI) in clinical medicine and healthcare, and to determine the prospects for its implementation to improve diagnosis, treatment, and medical data management.
Material and methods. A literature review on the main terms and concepts of AI, its classification by application area, technologies, and methodologies was carried out. The learning methods such as supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning were considered, as well as examples of AI application in various areas of medicine, including disease diagnosis and personalized medicine.
Results. AI shows significant potential in improving diagnosis, optimizing treatment processes, and managing healthcare resources. Main application areas are related to medical image analysis, developing individualized treatment plans, and healthcare management. However, using AI faces challenges such as data availability and bias, fragmentation of systems, and complexity of algorithm interpretation.
Conclusion. Despite the existing challenges, the implementation of AI in medicine has great prospects, including improved diagnostic accuracy, reduced task completion time, and development of personalized medicine. It is important to consider the ethical aspects and the demand for further study of AI application in medicine to achieve the best results.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2070-4933 (Online)